

WHY IT WORKS
A unique active ingredient makes ZUPREVO® (tildipirosin) effective, flexible and convenient.
ZUPREVO belongs to a class of antibiotics known as macrolides. Our active ingredient, tildipirosin, is a tri-basic, 16-member macrolide. This unique molecular structure allows ZUPREVO to last longer than competing BRD products.
Works against major BRD-causing bacteria.
- Mannheimia haemolytica
- Pasteurella multocida
- Histophilus somni
ZUPREVO excels where it matters.
When it comes to treating BRD and controlling respiratory disease, you want a product that acts fast, keeps working and delivers a big dose of BRD-fighting active ingredient to the lungs. Tildipirosin’s 16-member macrolide structure allows ZUPREVO to do all three.

ABSORBS FAST
Reaches peak plasma levels just 45 minutes after administration.2

LONG-LASTING
28 days*1 in the lungs. 21 days*1 in the bronchial fluid.

HIGH CONCENTRATION
Concentrates in the lungs and bronchial fluid, allowing extensive distribution.
*The correlation between pharmacokinetic data and clinical effectiveness is unknown.
Bactericidal Activity of Tildipirosin
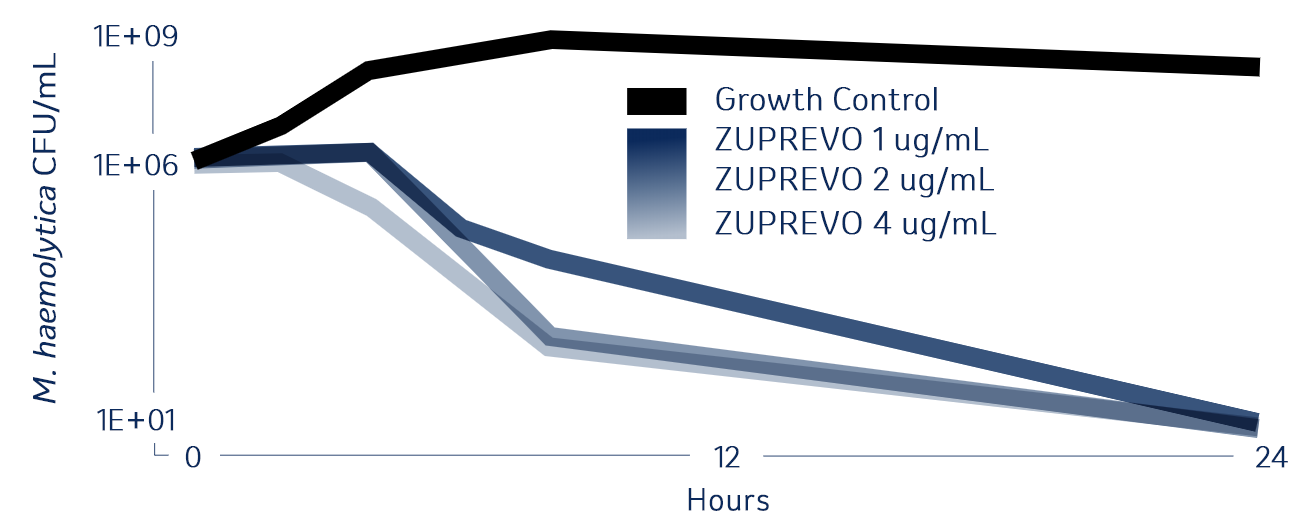
Get the BRD treatment that goes to work fast and stays working longer.
Residue Warning
Cattle intended for human consumption must not be slaughtered within 21 days of the last treatment. Do not use in female dairy cattle 20 months of age or older. Use of this drug product in these cattle may cause milk residues. A withdrawal period has not been established in pre-ruminating calves. Do not use in calves to be processed for veal.
Important Safety Information
Zuprevo: FOR USE IN ANIMALS ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN USE. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL INJECTION, DO NOT USE IN AUTOMATICALLY POWERED SYRINGES WHICH HAVE NO ADDITIONAL PROTECTION SYSTEM. IN CASE OF HUMAN INJECTION, SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE IMMEDIATELY AND SHOW THE PACKAGE INSERT OR LABEL TO THE PHYSICIAN. Cattle intended for human consumption must not be slaughtered within 21 days of the last treatment. Do not use in female dairy cattle 20 months of age or older. Use of this drug product in these cattle may cause milk residues. A withdrawal period has not been established in pre-ruminating calves. Do not use in calves to be processed for veal. The effects of Zuprevo®18% on bovine reproductive performance, pregnancy and lactation have not been determined. Swelling and inflammation, which may be severe, may be seen at the injection site after administration. Subcutaneous injection may result in local tissue reactions which persist beyond slaughter withdrawal period. This may result in trim loss of edible tissue at slaughter.
DO NOT USE Zuprevo®18% IN SWINE. Fatal adverse events have been reported following the use of tildipirosin in swine. NOT FOR USE IN CHICKENS OR TURKEYS.
References
- Menge M. et al. Pharmacokinetics of tildipirosin in bovine plasma, lung tissue, and bronchial fluid (from live, non-anesthetized cattle). J Vet Pharm Ther. Doj: 10.1111/J. 1365-2885, 2011. 1349.x.
- Wilhelm C (2009). Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentrations of 20, 23-di-piperidinyl-mycaminosyltylonlide against bacteria isolated from the respiratory tract of cattle suffering from respiratory disease isolated in different European countries between 2004 and 2008. Intervet-Doc. No. V-0045-0249.
- Stratton CW (2005). Molecular mechanisms of action for antimicrobial agents: General principles and mechanisms for selected classes of antibiotics. In V Lorian (ed). Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine. 5th ed., Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA, pp. 547-549. Intervet-Doc. No. V-0045-0444.
- Metz W (2005). Determination of the efficacy of P-MTMacrolide solution for injection in the treatment of experimentally induced Mannheimia haemolytica infection in cattle. Intervet-Doc. No. V-0045x-0017.
Contact
U.S. only: Merck Animal Health livestocktechsrvc@merck-animal-health.com or call 1-800-211-3574
For additional information, please see the product label.

Get the latest updates! Sign up to receive cattle health management insights, industry news and more sent straight to your inbox.
